Home
GridBagPanel
GridBagPanel
A scala.swing.GridBagPanel also arranges its elements in a grid. This grid, however, is not uniform, and Constraints are used to determine, for each element, which grid positions it should take, if it should be resized to fill the grid positions, and which grid rows and columns should be resized when the window is resized.
Here is an example:
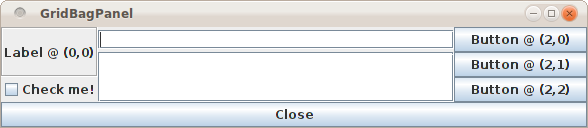
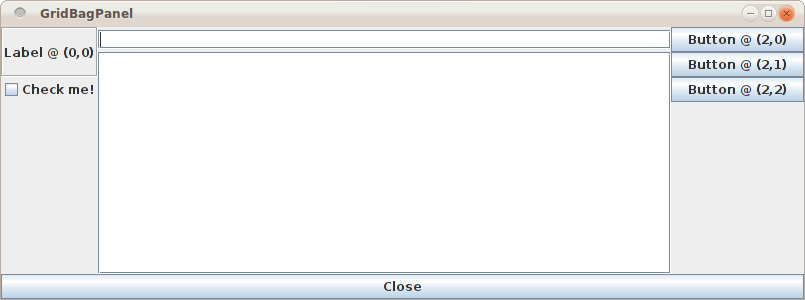
The source code for this example looks like this:
import scala.swing._
class UI extends MainFrame {
title = "GridBagPanel"
contents = new GridBagPanel {
def constraints(x: Int, y: Int,
gridwidth: Int = 1, gridheight: Int = 1,
weightx: Double = 0.0, weighty: Double = 0.0,
fill: GridBagPanel.Fill.Value = GridBagPanel.Fill.None)
: Constraints = {
val c = new Constraints
c.gridx = x
c.gridy = y
c.gridwidth = gridwidth
c.gridheight = gridheight
c.weightx = weightx
c.weighty = weighty
c.fill = fill
c
}
add(new Label("Label @ (0,0)") {border=Swing.EtchedBorder(Swing.Lowered) },
constraints(0, 0, gridheight=2, fill=GridBagPanel.Fill.Both))
add(new ToggleButton("Button @ (2,0)"),
constraints(2, 0))
add(new Button("Button @ (2,1)"),
constraints(2, 1))
add(new Button("Button @ (2,2)"),
constraints(2, 2))
add(new CheckBox("Check me!"),
constraints(0, 2))
add(new TextField { columns = 32 },
constraints(1, 0, weightx=1.0, fill=GridBagPanel.Fill.Horizontal))
add(new ScrollPane(new TextArea),
constraints(1, 1, gridheight=3, weighty = 1.0,
fill=GridBagPanel.Fill.Both))
add(Button("Close") { sys.exit(0) },
constraints(0, 4, gridwidth=3, fill=GridBagPanel.Fill.Horizontal))
}
}
object PanelFour {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val ui = new UI
ui.visible = true
}
}
As you can see, the layout is controlled by the Constraints
class (defined inside the GridBagPanel class). Its fields have
the following meaning:
- gridx and gridy specify the grid cell where the element should be placed;
- gridwidth and gridheight specify the number of grid cells that the element should span;
- weightx specifies how much this column should resize when the window is resized. The default is zero, meaning not to resize at all;
- weighty specifies how much this row should resize when the window is resized. The default is zero, meaning not to resize at all;
- fill specifies how the element should fill its space in the layout. Possible values are GridBagPanel.Fill.None, GridBagPanel.Fill.Horizontal, GridBagPanel.Fill.Vertical, and GridBagPanel.Fill.Both.
- anchor specifies where the element should be placed in its space. Some possible values are GridBagPanel.Anchor.North, GridBagPanel.Anchor.NorthEast, GridBagPanel.Anchor.Center, GridBagPanel.Anchor.SouthWest, and so on;
- ipadx and ipady can be used to increase the element's minimum size in x- and y-direction (the element is therefore increased in size);
- insets specifies extra space around the element, using an object of type java.awt.Insets