 |  |  | Spirit level |
Spirit level
In this project we will build a spirit level for Android, more precisely a Bull's eye level.The user interface is very simple: It consists of two concentric blue rings, and a red bubble. When the phone is held horizontal (for instance, if it is lying on a horizontal surface), the bubble should be exactly inside the smaller ring. The more the phone deviates from the horizontal position, the more the bubble moves away from the center (it rises to the part of the phone that is higher). Note that the bubble will never leave the outer blue ring (it always stays completely inside).
Here are two examples:
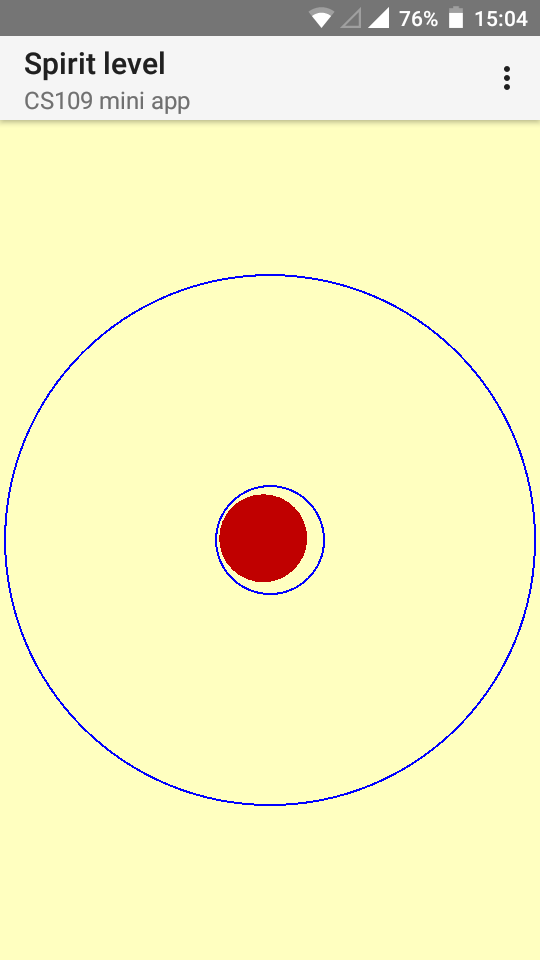
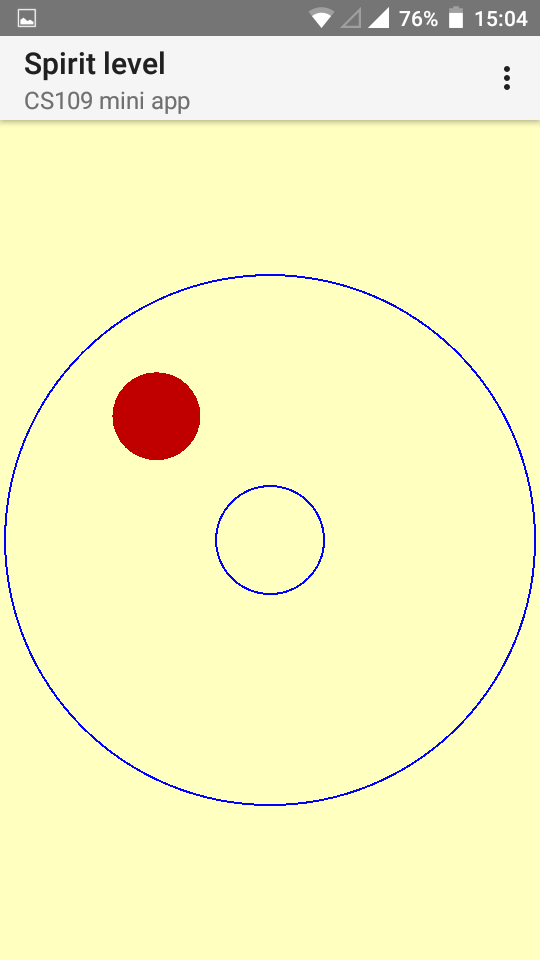
It makes sense to start your project from gravity1.kt.
The computations
Here is how I implemented the mathematics (But maybe you have a better way? Let me know!):
Starting with the \(x, y, z\) values from the accelerometer, normalize it by dividing each component by \(n = \sqrt{x^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2}}\).
Then, compute the angle \(\delta = \arccos(|z|)\). This is the angle by which the phone deviates from the horizontal position. In my implementation, the distance \(d\) of the red bubble from the center position is a linear function of \(\delta\). The maximum distance is reached for \(\pi / 8\).
It remains to compute the direction in which the red bubble moves away from the center. You can compute the angle \(\alpha = \arctan(-y/x)\) (use Math.atan2(-y, x)). Then the bubble position (measured from the screen center) is \((d \cos(\alpha), d \sin(\alpha))\).
Note
On my phone, it seems the acceleration sensor is not mounted completely aligned with the phone case. When I put my phone on a table, the red bubble is not exactly in the middle.
You may have the same problem—you can verify it by checking the accelerometer values using the gravity1.kt mini-app.
 |  |  | Spirit level |